살짝 괴상한 소리였긴 했지만 어쨌든 신기하군요! 이번엔 무엇이 저를 기다리고 있나요?
3장: 도형의 근사 (좌표평면)
원신의 페이몬
이 장에서는 xy평면에 그려진 도형을 푸리에 급수로 근사해 나타내는 방법을 탐구합니다.
코르
푸리에
이번엔, 좌표평면에 그려진 도형을 푸리에 급수로 근사해 나타내 보겠습니다.
아시다시피, 원은 좌표평면에서 r^2 = x^2 + y^2 으로 정의됩니다. 하지만, 매개변수로 표현하면, 원은 x = r * cos(t), y = r * sin(t)로 나타낼 수 있습니다.
같은 아이디어로, 좌표평면에 그려진 자취가 있다고 할 때 이것의 x좌표만을 모은 함수를 x(t), y좌표만을 모은 함수를 y(t)라고 해 봅시다.
그렇다면, x(t)를 푸리에 급수로 나타내고 y(t)를 푸리에 급수로 나타낸 후 근사하면 원래의 자취를 흉내낼 수 있을 것입니다.
1장에서처럼, html파일과 js파일을 만들고 1장과 동일하게 입력합니다...
이제, 푸리에 급수로 근사해 표현해 보고 싶은 사진을 고릅니다... 너무 복잡한 것 말구요.
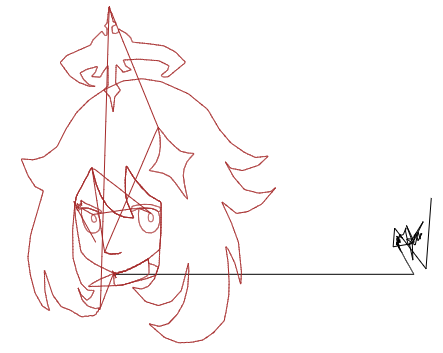
저는 이 사진을 골랐습니다.
※ 컴퓨터 게임 "원신" 으로부터의 스크린샷이며, 보이는 캐릭터는 "파이몬" 입니다.

이제 잉크스케이프를 열고, 사진을 붙여넣습니다.
이후 레이어를 추가합니다.

다음으로, 「베지어 직선과 곡선 그리기 도구」를 선택하고, 아래와 같이 윤곽선을 땁니다. 한붓그리기를 해도 되고 부분별로 따로 선을 따도 됩니다만, 결국에는 근사하는 과정에서 선이 모두 이어져 한붓그리기처럼 표현됩니다. 또한 아래 코드의 한계로 인해 곡선과 타원은 직선으로 표현되므로 이 점에 유의해서 작업을 해 주시면 되겠습니다.

다 되면 선만을 복사한 후 새 파일에 붙여넣고 저장합니다.
저장된 파일을 메모장으로 연 후, <path> 라고 적힌 모든 곳에서 d=이후의 값을 복사한 후, js파일에 아래와 같이 붙여넣습니다.

// 한붓그리기를 한 경우 경로 하나만 있을 것입니다.
// 부분별로 따로 선을 딴 경우 여러 개의 경로가 있을 것입니다.
const path1 = "m 0 0 l 10 10 ...";
const path2 = "m 10 10 h 20 v 20 ...";
// 한붓그리기를 한 경우 해당되지 않습니다.
const paimon = [path1, path2, ..., pathn].join(' ');
이제, 길고 긴 코드를 붙여넣읍시다 (직접 타이핑하기에는 너무 길어요). 또한 본 글의 주제와는 상관이 없으므로 코드를 이해하실 필요는 없습니다.
첫번째로 붙여넣을 코드는 위의 경로 데이터를 처리해서 x좌표 정보와 y좌표 정보만을 추출하는 코드입니다.
const refined = refineData(paimon);
const coords = extractCoords(refined);
const normalized = normalize(coords);
const populated = populate(normalized, 8);
const X = populated.x;
const Y = populated.y;
/**
* 경로 데이터를 정제해서 필요한 형태로 바꾸는 함수이다.
* @param {String} path_data 경로 데이터
* @returns {Array} 작도 명령(String)과 값들(String)이 프로퍼티로 들어있는 객체들의 배열
*/
function refineData(path_data) {
const pathSplitter = /([a-df-z])([^a-df-z]+)?/g;
const matches = path_data.matchAll(pathSplitter);
const result = [];
const paramSplitter = /[\s,]|\b(?=-)/;
for (const match of matches) {
const command = match[1];
const params = (match[2] ?? '').split(paramSplitter).filter(Boolean);
result.push({ command, params });
}
return result;
}
/**
* 정제된 데이터로부터 좌표를 추출하는 함수이다.
* ※ 2차, 3차 베지어 곡선과 타원은 직선으로 처리된다.
* @param {Array} refined 작도 명령(String)과 값들(String)이 프로퍼티로 들어있는 객체들의 배열
* @returns {{ x: Array, y: Array }} 좌표 정보가 담긴 객체
*/
function extractCoords(refined) {
if (refined[0].command !== 'm' && refined[0].command !== 'M') {
throw new Error('유효하지 않은 첫번째 작도 명령: 첫번째 명령은 반드시 m 또는 M으로 시작해야 합니다.');
}
const x = [];
const y = [];
const originPoint = { x: Number(refined[0].params[0]), y: Number(refined[0].params[1]) };
const initialPoint = { x: undefined, y: undefined };
for (let i = 0; i < refined.length; i++) {
switch (refined[i].command) {
case 'M': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: M`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const xIdx = j;
const yIdx = j + 1;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]) - originPoint.x);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
initialPoint.x = x.at(-paramLen / 2);
initialPoint.y = y.at(-paramLen / 2);
break;
}
case 'm': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: m`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const xIdx = j;
const yIdx = j + 1;
if (j === 0) {
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]) - originPoint.y);
} else {
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]));
}
}
initialPoint.x = x.at(-paramLen / 2);
initialPoint.y = y.at(-paramLen / 2);
break;
}
case 'L': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: L`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const xIdx = j;
const yIdx = j + 1;
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 'l': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: l`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const xIdx = j;
const yIdx = j + 1;
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'H': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[j]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(y.at(-1));
}
break;
}
case 'h': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[j]));
y.push(y.at(-1));
}
break;
}
case 'V': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
x.push(x.at(-1));
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[j]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 'v': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
x.push(x.at(-1));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[j]));
}
break;
}
case 'C': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 6 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: C`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 6) {
const endXIdx = j + 4;
const endYIdx = j + 5;
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 'c': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 6 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: c`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 6) {
const endXIdx = j + 4;
const endYIdx = j + 5;
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'S': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: S`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endXIdx = j + 2;
const endYIdx = j + 3;
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 's': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: s`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endXIdx = j + 2;
const endYIdx = j + 3;
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'Q': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: Q`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endXIdx = j + 2;
const endYIdx = j + 3;
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 'q': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: q`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endXIdx = j + 2;
const endYIdx = j + 3;
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'T': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: T`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const endXIdx = j;
const endYIdx = j + 1;
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 't': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: t`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const endXIdx = j;
const endYIdx = j + 1;
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endXIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endYIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'A': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 7 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: A`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 7) {
const xIdx = j + 5;
const yIdx = j + 6;
x.push(Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]) - originPoint.x);
y.push(Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]) - originPoint.y);
}
break;
}
case 'a': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 7 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: a`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 7) {
const xIdx = j + 5;
const yIdx = j + 6;
x.push(x.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[xIdx]));
y.push(y.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[yIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'Z': {
x.push(initialPoint.x);
y.push(initialPoint.y);
break;
}
case 'z': {
x.push(initialPoint.x);
y.push(initialPoint.y);
break;
}
default: throw new Error('좌표 추출 중 예외 발생: 올바르지 않은 작도 명령이 포함되었을 가능성이 있습니다.');
}
}
return { x, y };
}
/**
* 좌표의 값을 [-1, 1] 사이로 맞추는 함수이다.
* 데이터에 따라 숫자의 크기가 달라지는 걸 방지하기 위해서이고,
* 혹시라도 큰 수가 들어오는 것을 방지하기 위함이다.
* @param {{ x: Array, y: Array }} coords 좌표 정보
* @returns {{ x: Array, y: Array }} 값이 조정된 좌표 정보
*/
function normalize(coords) {
const x = [];
const y = [];
const maxX = Math.max(...coords.x);
const minX = Math.min(...coords.x);
const biggestX = Math.max(Math.abs(maxX), Math.abs(minX));
const maxY = Math.max(...coords.y);
const minY = Math.min(...coords.y);
const biggestY = Math.max(Math.abs(maxY), Math.abs(minY));
for (let t = 0; t < coords.x.length; t++) {
x[t] = coords.x[t] / biggestX;
y[t] = coords.y[t] / biggestY;
}
return { x, y };
}
/**
* 값과 값 사이에 값을 넣어 데이터를 조밀하게 만드는 함수이다.
* 결과로 나오는 그림이 부드럽게 보이게 만든다.
* @param {{ x: Array, y: Array}} coords 좌표 정보
* @param {Number} n 값과 값 사이에 몇 개의 값을 채울 것인가?
* @returns {{ x: Array, y: Array }} 조밀하게 구성된 좌표 정보
*/
function populate(coords, n) {
if (coords.x.length <= 1) throw new Error('값을 채우기에 데이터가 충분하지 않습니다. 최소한 2 이상이어야 합니다.');
if (n < 1) throw new Error('값 사이에 채우고자 하는 값들의 수가 적절하지 않습니다. 최소 1 이상의 양수여야 합니다.');
const x = new Array(coords.x.length + (coords.x.length - 1) * n);
const y = new Array(coords.y.length + (coords.y.length - 1) * n);
for (let t = 0; t < coords.x.length; t++) {
x[t * (n + 1)] = coords.x[t];
y[t * (n + 1)] = coords.y[t];
}
for (let t = 0; t <= (x.length - n - 2); t += (n + 1)) {
const reInterpolation = (x[t + n + 1] - x[t]) / (n + 1);
const imInterpolation = (y[t + n + 1] - y[t]) / (n + 1);
for (let u = 1; u <= n; u++) {
x[t + u] = x[t] + reInterpolation * u;
y[t + u] = y[t] + imInterpolation * u;
}
}
return { x, y };
}
다음으로는 수학에 관련된 코드를 작성합니다. 이 부분은 중요하니 주의 깊게 살펴볼 필요가 있습니다.
/**
* 리만 합을 구하는 함수 (수치적분; 사각형을 사용한 넓이 근사)
* @param {Number} start 적분 시작 위치
* @param {Number} end 적분 끝 위치
* @param {Number} division [step, step + 1) 를 몇 등분하는가?
* @param {Function} f 적분할 함수
* @returns {Number} 적분값
*/
function integrate(start, end, division, f) {
if (division < 1) throw new Error('분할 갯수는 1 미만일 수 없습니다.');
let sum = 0;
const STEP = 1 / division;
for (let t = start; t < end; t += STEP) {
sum += f(t) * STEP;
}
return sum;
}
// a0, an, bn
class Coef {
// Coef의 생성자 함수
constructor(num = 99) {
this.num = num;
this.a0 = undefined;
this.an = [];
this.bn = [];
}
/**
* a0값을 구하는 함수이다.
* @param {Function} f
* @param {Number} period
* @param {Number} division
*/
getA0(f, period, division) {
this.a0 = (1 / period) * integrate(0, period, division, (t) => f(t));
}
/**
* an값을 구하는 함수이다.
* @param {Function} f
* @param {Number} period
* @param {Number} division
*/
getAn(f, period, division) {
const w = 2 * Math.PI / period;
for (let n = 1; n <= this.num; n++) {
const anValue = (2 / period) * integrate(0, period, division, (t) => f(t) * Math.cos(n * w * t));
this.an.push(anValue);
}
}
/**
* bn값을 구하는 함수이다.
* @param {Function} f
* @param {Number} period
* @param {Number} division
*/
getBn(f, period, division) {
const w = 2 * Math.PI / period;
for (let n = 1; n <= this.num; n++) {
const bnValue = (2 / period) * integrate(0, period, division, (t) => f(t) * Math.sin(n * w * t));
this.bn.push(bnValue);
}
}
}
메서드 getA0, getAn, getBn을 보면 1장에서 봤던 수식이 그대로 들어있는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 이 함수들이 푸리에 급수를 계산합니다.
다음으로는 푸리에 계수를 얻습니다.
// x 좌표의 갯수를 하나의 주기로 봄
// 당연한 말이지만, x 좌표의 갯수와 y 좌표의 갯수는 동일함
// 배열의 값을 읽을 때 Math.floor (= 내림) 을 한 이유는 배열은 이산적이므로 그 사이의 값이 존재하지 않기 때문임.
const xCoef = new Coef(999);
xCoef.getA0((t) => X[Math.floor(t)], X.length, 10);
xCoef.getAn((t) => X[Math.floor(t)], X.length, 10);
xCoef.getBn((t) => X[Math.floor(t)], X.length, 10);
const yCoef = new Coef(999);
yCoef.getA0((t) => Y[Math.floor(t)], Y.length, 10);
yCoef.getAn((t) => Y[Math.floor(t)], Y.length, 10);
yCoef.getBn((t) => Y[Math.floor(t)], Y.length, 10);
"왜 푸리에 계수가 2개 있나요?" 위에서 푸리에 선생님께서 말씀하셨듯, x(t)와 y(t)에 대해 각각 푸리에 급수 전개를 실시했기 때문입니다.
※ 연산량이 많아서 그런지 컴퓨터가 좀 힘들어 할 수도 있습니다.
다음으로는 canvas 요소에 그림을 그리는 코드를 작성합니다. x성분과 y성분이 있으므로, 두 그룹으로 나누어 그려 봅시다.
const $cvs = document.getElementById('cvs');
const cctx = $cvs.getContext('2d');
const scaler = 200;
const xOffset = { x: 200, y: 600 };
const yOffset = { x: 600, y: 200 };
const path = [];
let t = 0;
window.requestAnimationFrame(drawShape);
function drawShape() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(drawShape);
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, $cvs.width, $cvs.height);
// x성분
let x = 0;
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
x += scaler * xCoef.a0;
cctx.lineTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
cctx.stroke();
for (let i = 0; i < xCoef.an.length; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
x += scaler * xCoef.an[i] * Math.cos((i + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
cctx.lineTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
cctx.stroke();
}
for (let i = 0; i < xCoef.bn.length; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
x += scaler * xCoef.bn[i] * Math.sin((i + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
cctx.lineTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
cctx.stroke();
}
// y 성분
let y = 0;
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
y += scaler * yCoef.a0;
cctx.lineTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
cctx.stroke();
for (let i = 0; i < yCoef.an.length; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
y += scaler * yCoef.an[i] * Math.cos((i + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / Y.length);
cctx.lineTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
cctx.stroke();
}
for (let i = 0; i < yCoef.bn.length; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
y += scaler * yCoef.bn[i] * Math.sin((i + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / Y.length);
cctx.lineTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
cctx.stroke();
}
// x성분과 y성분의 조우점
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.moveTo(yOffset.x + 0, yOffset.y + y);
cctx.lineTo(xOffset.x + x, yOffset.y + y);
cctx.stroke();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.moveTo(xOffset.x + x, xOffset.y + 0);
cctx.lineTo(xOffset.x + x, yOffset.y + y);
cctx.stroke();
// 이 조우점이 자취의 좌표임
path.push({ x, y });
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(xOffset.x + path[0].x, yOffset.y + path[0].y);
for (let i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
cctx.lineTo(xOffset.x + path[i].x, yOffset.y + path[i].y);
}
cctx.stroke();
if (t === X.length) {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
} else {
t++;
}
}
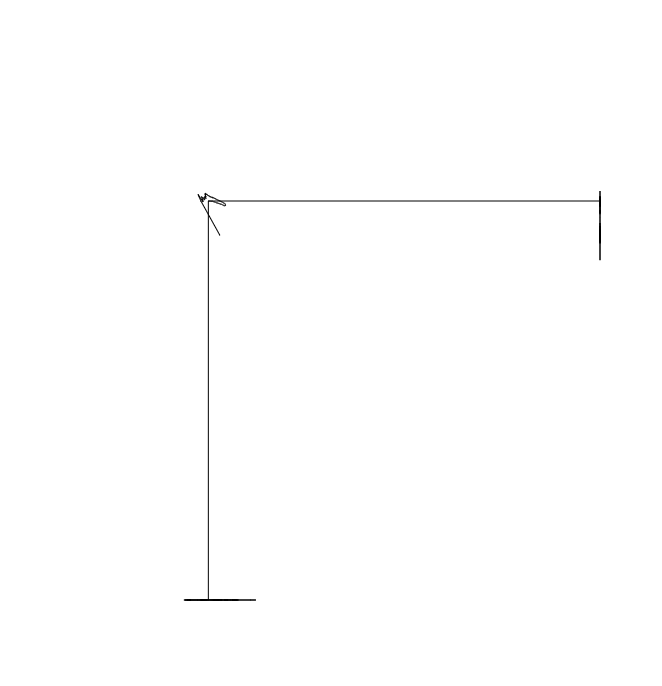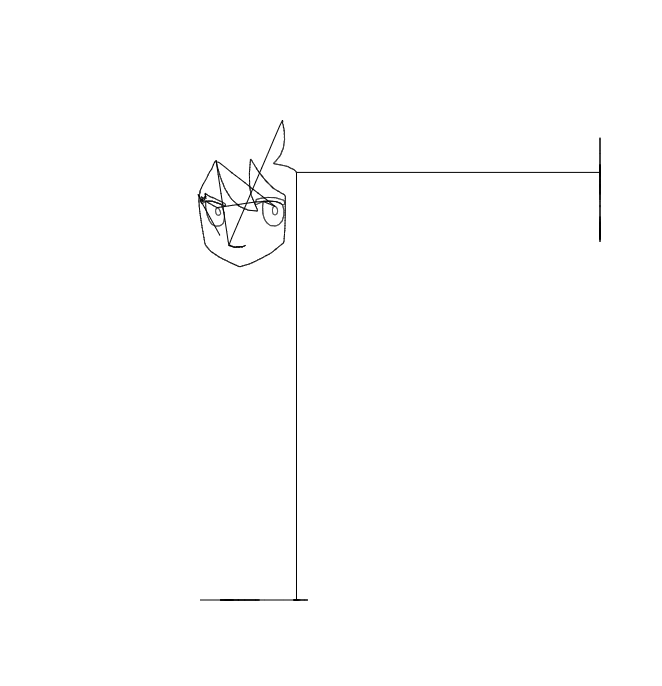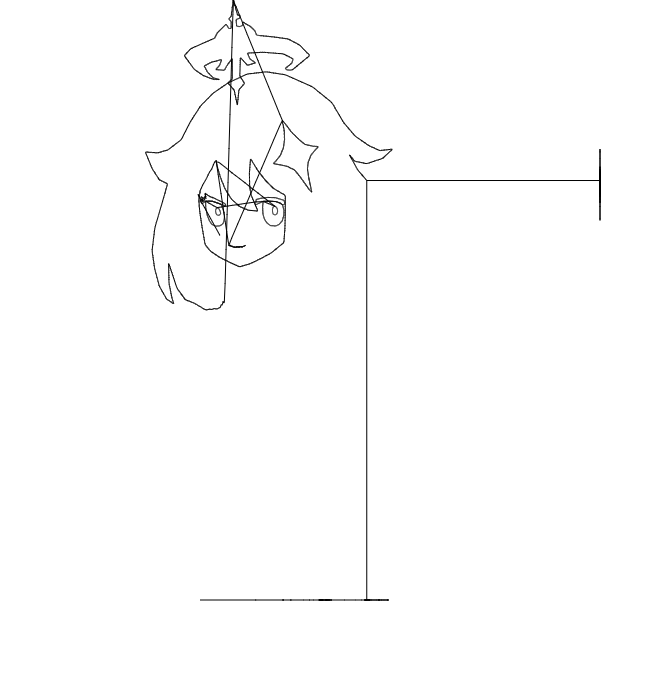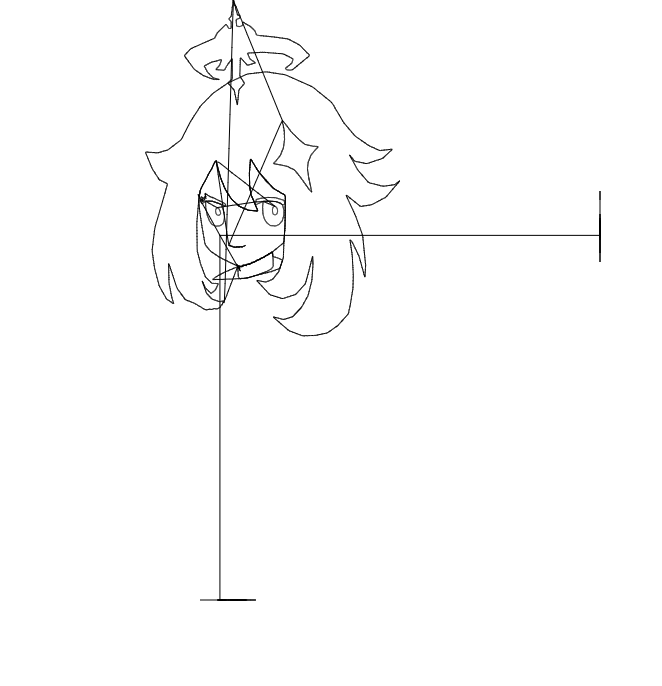
결과는 다음 gif와 같습니다.
x성분과 y성분을 하나로 합쳐도 됩니다. 방금 위에서 추가한 코드를 지우고 아래의 코드를 붙여넣읍시다.
const $cvs = document.getElementById('cvs');
const cctx = $cvs.getContext('2d');
const offset = { x: 600, y: 300 };
const shapeOffset = 300;
const scaler = 200;
let t = 0;
const path = [];
window.requestAnimationFrame(drawShape);
function drawShape() {
rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(drawShape);
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, $cvs.width, $cvs.height);
const v = { x: xCoef.a0, y: yCoef.a0 };
for (let n = 0; n < xCoef.num; n++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.x, offset.y + v.y);
// 중요! x(t)와 y(t)의 푸리에 급수 계산 결과를 v.x와 v.y에 더하는 것입니다.
v.x += scaler * xCoef.an[n] * Math.cos((n + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
v.x += scaler * xCoef.bn[n] * Math.sin((n + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
v.y += scaler * yCoef.an[n] * Math.cos((n + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
v.y += scaler * yCoef.bn[n] * Math.sin((n + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.x, offset.y + v.y);
cctx.stroke();
}
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.x, offset.y + v.y);
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.x - shapeOffset, offset.y + v.y);
cctx.stroke();
path.push({ x: v.x - shapeOffset, y: v.y });
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'brown';
for (let i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
if (i === 0) {
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + path[0].x, offset.y + path[0].y);
} else {
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + path[i].x, offset.y + path[i].y);
}
}
cctx.stroke();
if (t === X.length - 1) {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
} else {
t++;
}
}
결과는 아래 gif와 같습니다.
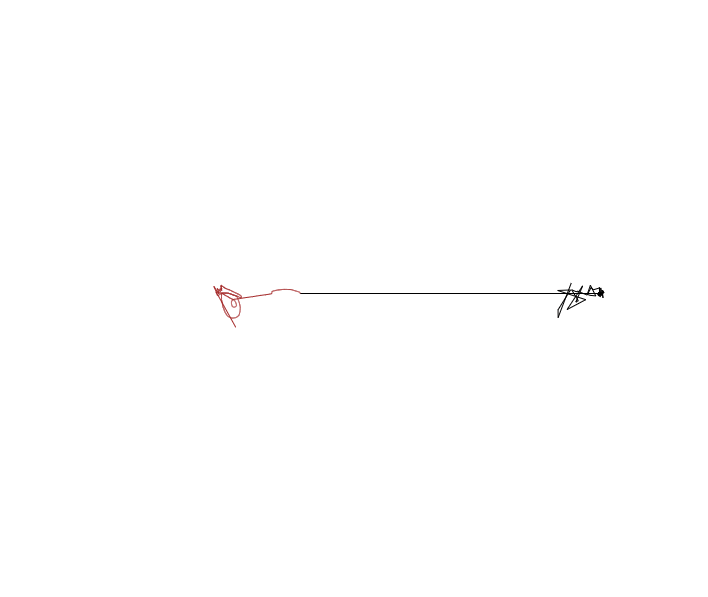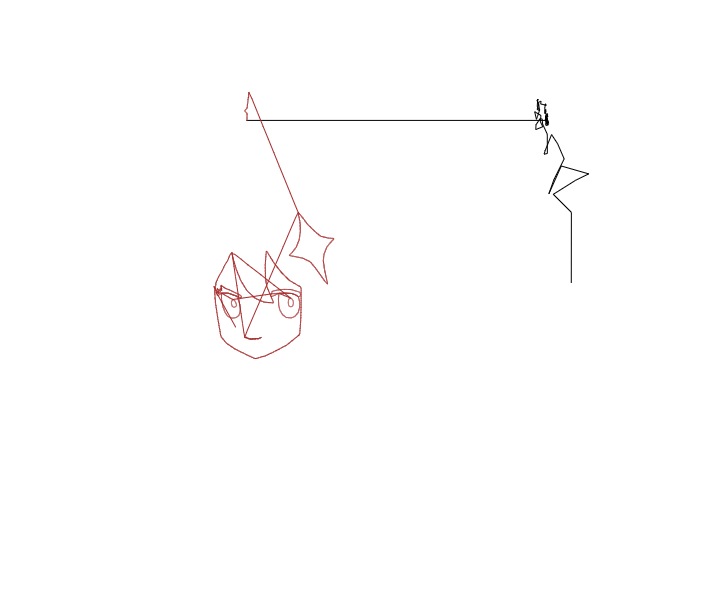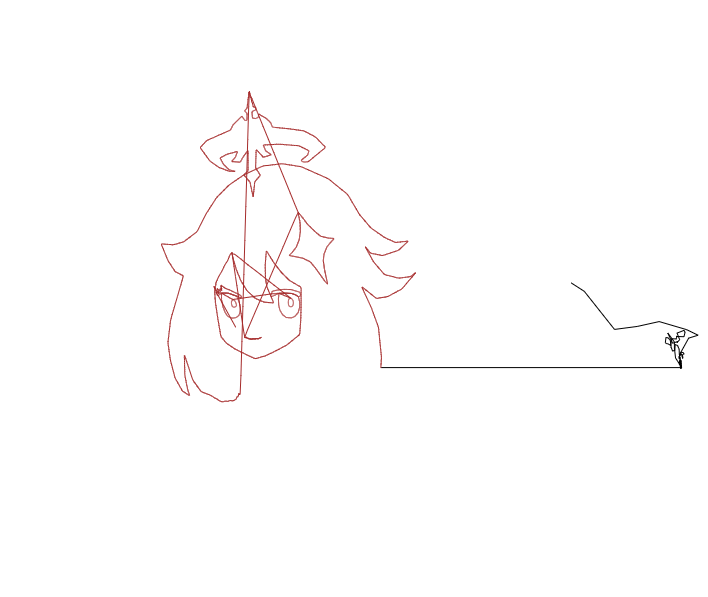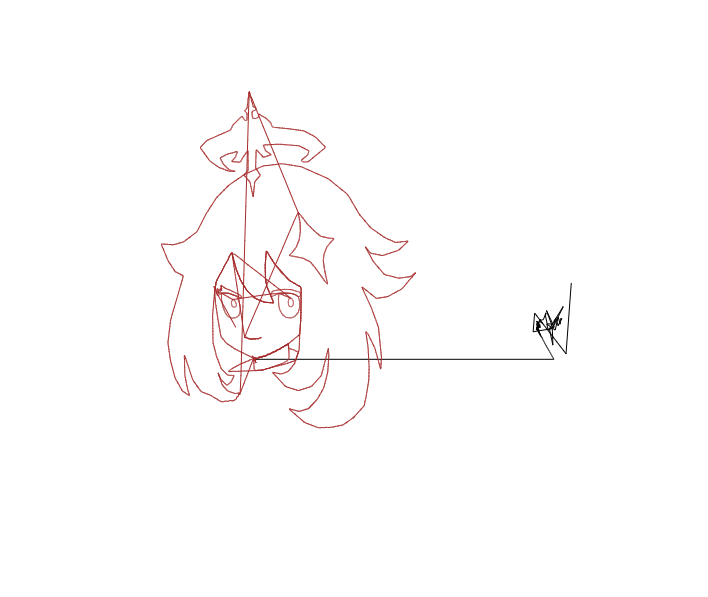
코르
와! 페이몬이 정말 귀여워요! 역시 근사되어도 그 미모는 어디 가지 않는군요!
푸리에
ㄹㅇㅋㅋ
또 한 가지 재미있는 것은 시간에 따른 원래의 x(t), y(t) 추이와 근사된 푸리에 급수의 추이를 대조해보는 것입니다.
아래는 계수가 99개 (a0 미포함) 일 때의 x(t)와 근사된 x(t)의 추이입니다.
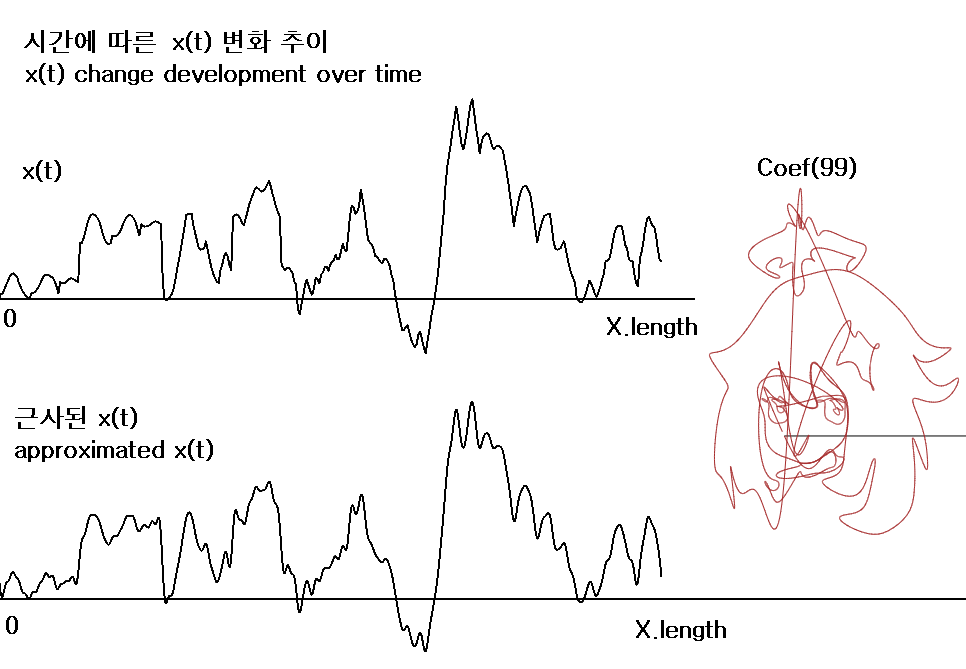
function f(t) {
let anSum = 0;
let bnSum = 0;
for (let n = 0; n < xCoef.an.length; n++) {
anSum += xCoef.an[n] * Math.cos((n + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
bnSum += xCoef.bn[n] * Math.sin((n + 1) * 2 * Math.PI * t / X.length);
}
return xCoef.a0 + anSum + bnSum;
}
function xChanges() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(xChanges);
// 선 1
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.moveTo(0, 300);
cctx.lineTo($cvs.width, 300);
cctx.stroke();
// 선 2
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.moveTo(0, 600);
cctx.lineTo($cvs.width, 600);
cctx.stroke();
// x(t)
cctx.beginPath();
for (let x = 0; x < X.length; x++) {
if (x === 0) cctx.moveTo(x * 0.2, 300 - scaler * X[x]);
else cctx.lineTo(x * 0.2, 300 - scaler * X[x]);
}
cctx.stroke();
// 근사된 x(t)
cctx.beginPath();
for (let x = 0; x < X.length; x++) {
if (x === 0) cctx.moveTo(x * 0.2, 600 - scaler * f(x));
else cctx.lineTo(x * 0.2, 600 - scaler * f(x));
}
cctx.stroke();
if (t === X.length - 1) {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
} else {
t++;
}
}
직접 그려보시려면 위 단락의 코드를 붙여넣은 후 다음을 변경해 보세요.
// 이것을
window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_shape);
// 이걸로 변경
window.requestAnimationFrame(xChanges);