좌표평면에서의 근사는 잘 보았습니다. 근데 한 가지 방법이 더 있다고 하셨습니까?
4장: 도형의 근사 (복소평면)
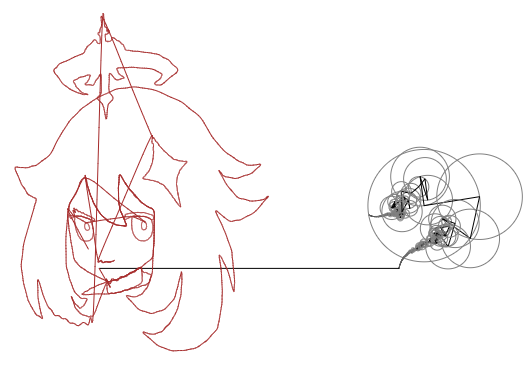
원신의 페이몬
이 장에서는 복소평면에 그려진 도형을 푸리에 급수로 근사해 나타내는 방법을 탐구합니다.
코르
푸리에
그렇습니다. 이전 장에서는 도형을 좌표평면에 그려진 것으로 보고 도형의 자취를 x(t)와 y(t)로 나눴습니다만, 이번에는 도형이 복소평면에 그려진 것으로 보고 점의 자취를 p(t) = x(t) + iy(t)로 생각합니다.
좌표평면에서의 근사의 경우 복소평면과는 다르게 애초에 도형의 자취를 하나의 함수로 볼 수 없었기 때문에, x 성분과 y 성분에 대해 각각 푸리에 전개할 수 밖에 없었고, 이에 두 개의 푸리에 급수가 생겨났습니다. 즉 이 푸리에 급수들은 '원래의 도형' 을 근사한 것이 아니라 x(t), 즉 t에 따른 x값의 변화와, y(t), 즉 t에 따른 y값의 변화를 근사한 것에 지나지 않습니다. 요컨대 원래의 그림을 재현하려면 '근사된 x(t)와 y(t)'로부터 '급수의 합으로서 계산된 x와 y값'만을 가져오지 않으면 안됩니다. 한편, 복소평면에서는 하나의 식에 실수 성분과 허수 성분이 모두 포함되어 있으므로 하나의 푸리에 급수의 계산 결과로 도형을 근사할 수 있게 됩니다.
코르
계산을 해 보니 푸리에 급수도 실수와 허수 성분의 합으로 이루어져 있는 것을 알 수 있었습니다!
(아래는 Cn의 식입니다.)

(아래는 푸리에 급수입니다.)

이제 실습해 보겠습니다. 이전처럼 html파일과 js파일을 생성한 뒤, js파일에 아래의 코드를 붙여넣습니다.
svg 경로 데이터는 3장과 동일한 것을 사용하시면 됩니다.
svg 경로 데이터를 가져와 좌표를 추출하는 과정은 3장과 동일합니다.
const refined = refineData(「경로 데이터」);
const coords = extractCoords(refined);
const normalized = normalize(coords);
const populated = populate(normalized, 8);
const RE = populated.re;
const IM = populated.im;
/**
* 경로 데이터를 정제해서 필요한 형태로 바꾸는 함수이다.
* @param {String} path_data 경로 데이터
* @returns {Array} 작도 명령(String)과 값들(String)이 프로퍼티로 들어있는 객체들의 배열
*/
function refineData(path_data) {
const pathSplitter = /([a-df-z])([^a-df-z]+)?/g;
const matches = path_data.matchAll(pathSplitter);
const result = [];
const paramSplitter = /[\s,]|\b(?=-)/;
for (const match of matches) {
const command = match[1];
const params = (match[2] ?? '').split(paramSplitter).filter(Boolean);
result.push({ command, params });
}
return result;
}
/**
* 정제된 데이터로부터 좌표를 추출하는 함수이다.
* ※ 2차, 3차 베지어 곡선과 타원은 직선으로 처리된다.
* @param {Array} refined 작도 명령(String)과 값들(String)이 프로퍼티로 들어있는 객체들의 배열
* @returns {{ re: Array, im: Array }} 좌표 정보가 담긴 객체
*/
function extractCoords(refined) {
if (refined[0].command !== 'm' && refined[0].command !== 'M') {
throw new Error('유효하지 않은 첫번째 작도 명령: 첫번째 명령은 반드시 m 또는 M으로 시작해야 합니다.');
}
const re = [];
const im = [];
const originPoint = { re: Number(refined[0].params[0]), im: Number(refined[0].params[1]) };
const initialPoint = { re: undefined, im: undefined };
for (let i = 0; i < refined.length; i++) {
switch (refined[i].command) {
case 'M': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: M`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const reIdx = j;
const imIdx = j + 1;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
initialPoint.re = re.at(-paramLen / 2);
initialPoint.im = im.at(-paramLen / 2);
break;
}
case 'm': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: m`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const reIdx = j;
const imIdx = j + 1;
if (j === 0) {
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]) - originPoint.im);
} else {
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]));
}
}
initialPoint.re = re.at(-paramLen / 2);
initialPoint.im = im.at(-paramLen / 2);
break;
}
case 'L': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: L`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const reIdx = j;
const imIdx = j + 1;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 'l': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: l`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const reIdx = j;
const imIdx = j + 1;
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'H': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[j]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(im.at(-1));
}
break;
}
case 'h': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[j]));
im.push(im.at(-1));
}
break;
}
case 'V': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
re.push(re.at(-1));
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[j]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 'v': {
for (let j = 0; j < refined[i].params.length; j++) {
re.push(re.at(-1));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[j]));
}
break;
}
case 'C': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 6 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: C`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 6) {
const endReIdx = j + 4;
const endImIdx = j + 5;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 'c': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 6 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: c`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 6) {
const endReIdx = j + 4;
const endImIdx = j + 5;
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'S': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: S`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endReIdx = j + 2;
const endImIdx = j + 3;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 's': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: s`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endReIdx = j + 2;
const endImIdx = j + 3;
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'Q': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: Q`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endReIdx = j + 2;
const endImIdx = j + 3;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 'q': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 4 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: q`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 4) {
const endReIdx = j + 2;
const endImIdx = j + 3;
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'T': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: T`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const endReIdx = j;
const endImIdx = j + 1;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 't': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 2 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: t`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 2) {
const endReIdx = j;
const endImIdx = j + 1;
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endReIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[endImIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'A': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 7 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: A`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 7) {
const reIdx = j + 5;
const imIdx = j + 6;
re.push(Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]) - originPoint.re);
im.push(Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]) - originPoint.im);
}
break;
}
case 'a': {
const paramLen = refined[i].params.length;
if (paramLen % 7 !== 0) throw new Error(`올바르지 않은 파라미터 갯수: ${i}번째 명령; 유형: a`);
for (let j = 0; j < paramLen; j += 7) {
const reIdx = j + 5;
const imIdx = j + 6;
re.push(re.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[reIdx]));
im.push(im.at(-1) + Number(refined[i].params[imIdx]));
}
break;
}
case 'Z': {
re.push(initialPoint.re);
im.push(initialPoint.im);
break;
}
case 'z': {
re.push(initialPoint.re);
im.push(initialPoint.im);
break;
}
default: throw new Error('좌표 추출 중 예외 발생: 올바르지 않은 작도 명령이 포함되었을 가능성이 있습니다.');
}
}
return { re, im };
}
/**
* 좌표의 값을 [-1, 1] 사이로 맞추는 함수이다.
* 데이터에 따라 숫자의 크기가 달라지는 걸 방지하기 위해서이고,
* 혹시라도 큰 수가 들어오는 것을 방지하기 위함이다.
* @param {{ re: Array, im: Array }} coords 좌표 정보
* @returns {{ re: Array, im: Array }} 값이 조정된 좌표 정보
*/
function normalize(coords) {
const re = [];
const im = [];
const maxRe = Math.max(...coords.re);
const minRe = Math.min(...coords.re);
const biggestRe = Math.max(Math.abs(maxRe), Math.abs(minRe));
const maxIm = Math.max(...coords.im);
const minIm = Math.min(...coords.im);
const biggestIm = Math.max(Math.abs(maxIm), Math.abs(minIm));
for (let t = 0; t < coords.re.length; t++) {
re[t] = coords.re[t] / biggestRe;
im[t] = coords.im[t] / biggestIm;
}
return { re, im };
}
/**
* 값과 값 사이에 값을 넣어 데이터를 조밀하게 만드는 함수이다.
* 결과로 나오는 그림이 부드럽게 보이게 만든다.
* @param {{ re: Array, im: Array}} coords 좌표 정보
* @param {Number} n 값과 값 사이에 몇 개의 값을 채울 것인가?
* @returns {{ re: Array, im: Array }} 조밀하게 구성된 좌표 정보
*/
function populate(coords, n) {
if (coords.re.length <= 1) throw new Error('값을 채우기에 데이터가 충분하지 않습니다. 최소한 2 이상이어야 합니다.');
if (n < 1) throw new Error('값 사이에 채우고자 하는 값들의 수가 적절하지 않습니다. 최소 1 이상의 양수여야 합니다.');
const re = new Array(coords.re.length + (coords.re.length - 1) * n);
const im = new Array(coords.im.length + (coords.im.length - 1) * n);
for (let t = 0; t < coords.re.length; t++) {
re[t * (n + 1)] = coords.re[t];
im[t * (n + 1)] = coords.im[t];
}
for (let t = 0; t <= (re.length - n - 2); t += (n + 1)) {
const reInterpolation = (re[t + n + 1] - re[t]) / (n + 1);
const imInterpolation = (im[t + n + 1] - im[t]) / (n + 1);
for (let u = 1; u <= n; u++) {
re[t + u] = re[t] + reInterpolation * u;
im[t + u] = im[t] + imInterpolation * u;
}
}
return { re, im };
}
아래는 위 사진에서 구한 식을 코드로 옮긴 것입니다. (수치적분 함수는 이전과 동일합니다)
/**
* 리만 합을 구하는 함수 (수치적분; 사각형을 사용한 넓이 근사)
* @param {Number} start 적분 시작 위치
* @param {Number} end 적분 끝 위치
* @param {Number} division [step, step + 1) 를 몇 등분하는가?
* @param {Function} f 적분할 함수
* @returns {Number} 적분값
*/
function integrate(start, end, division, f) {
if (division < 1) throw new Error('분할 갯수는 1 미만일 수 없습니다.');
let sum = 0;
const STEP = 1 / division;
for (let t = start; t < end; t += STEP) {
sum += f(t) * STEP;
}
return sum;
}
// cn
class Cn {
// Cn의 생성자 함수
constructor(num = 100) {
this.num = num;
this.re = [];
this.im = [];
}
get num() {
return this._num;
}
// num 프로퍼티 설정자
set num(value) {
if (value % 2 !== 0) throw new Error('계수의 갯수는 짝수여야 합니다.');
this._num = value;
}
/**
* 계수를 계산하는 함수이다.
* @param {Function} fr 실수항
* @param {Function} fi 허수항
* @param {Number} period 한 주기
* @param {Number} division 수치 적분 정밀도
*/
getCoef(fr, fi, period, division) {
const half = this._num / 2;
const w = 2 * Math.PI / period;
for (let n = -half; n <= half; n++) {
const reValue = (1 / period) * integrate(0, period, division, (t) => fr(t) * Math.cos(n * w * t) + fi(t) * Math.sin(n * w * t));
const imValue = (1 / period) * integrate(0, period, division, (t) => fi(t) * Math.cos(n * w * t) - fr(t) * Math.sin(n * w * t));
this.re.push(reValue);
this.im.push(imValue);
}
}
}
이제 계수 cn을 구합니다.
const cn = new Cn(1000);
cn.getCoef((t) => RE[Math.floor(t)], (t) => IM[Math.floor(t)], RE.length, 10);
이제 캔버스 코드를 작성합니다.
const $cvs = document.getElementById('cvs');
const cctx = $cvs.getContext('2d');
const offset = { x: 600, y: 300 };
const shapeOffset = 300;
const scaler = 200;
let deg = 0;
const path = [];
window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_shape);
function draw_shape() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_shape);
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, $cvs.width, $cvs.height);
const v = { re: 0, im: 0 };
for (let i = 0; i < cn.num + 1; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'gray';
const r = Math.sqrt((scaler * cn.re[i]) ** 2 + (scaler * cn.im[i]) ** 2);
cctx.arc(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im, r, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
// 회전변환
v.re += scaler * cn.re[i] * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length) - scaler * cn.im[i] * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length);
v.im += scaler * cn.re[i] * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length) + scaler * cn.im[i] * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length);
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.stroke();
}
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.re - shapeOffset, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.stroke();
path.push({ re: v.re - shapeOffset, im: v.im });
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'brown';
for (let i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
if (i === 0) {
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + path[0].re, offset.y + path[0].im);
} else {
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + path[i].re, offset.y + path[i].im);
}
}
cctx.stroke();
if (deg === RE.length - 1) {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
} else {
deg++;
}
}
결과는 아래 gif와 같습니다.
지난 3장과는 다르게 이번엔 '원'이 있고 '반지름'도 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 이는 실수부 벡터와 허수부 벡터의 합벡터입니다. 3장에서는 도형 자체를 근사한 것이 아니라 도형의 좌표 함수를 근사한 것이기 때문에 '도형'을 푸리에 급수를 이루는 기본 파동들의 회전으로 나타낼 수 없었습니다. 반면 이번에는 도형 자체를 근사했으므로 푸리에 급수를 이루는 기본 파동들의 회전을 나타낼 수 있기 때문에 원으로 표현가능합니다. 이것이 근본적인 차이입니다.
아래처럼 실수성분의 움직임과 허수성분의 움직임을 따로 나타내볼 수도 있습니다: (직접 그려보시려면 방금 추가한 코드를 삭제하고 아래 코드 추가)
const $cvs = document.getElementById('cvs');
const cctx = $cvs.getContext('2d');
const offset = { x: 600, y: 300 };
const shapeOffset = 300;
const scaler = 200;
let deg = 0;
const path = [];
window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_shape);
function draw_shape() {
const rAF = window.requestAnimationFrame(draw_shape);
cctx.clearRect(0, 0, $cvs.width, $cvs.height);
const v = { re: 0, im: 0 };
for (let i = 0; i < cn.num + 1; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'gray';
const r = Math.abs(scaler * cn.re[i]);
cctx.arc(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im, r, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
v.re += scaler * cn.re[i] * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length) - scaler * cn.im[i] * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length);
v.im += 0;
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.stroke();
}
for (let i = 0; i < cn.num + 1; i++) {
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'gray';
const r = Math.abs(scaler * cn.im[i]);
cctx.arc(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im, r, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
cctx.stroke();
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
v.re += 0;
v.im += scaler * cn.re[i] * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length) + scaler * cn.im[i] * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * deg * (i - cn.num / 2) / RE.length);
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.stroke();
}
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + v.re, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + v.re - shapeOffset, offset.y + v.im);
cctx.stroke();
path.push({ re: v.re - shapeOffset, im: v.im });
cctx.beginPath();
cctx.strokeStyle = 'brown';
for (let i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
if (i === 0) {
cctx.moveTo(offset.x + path[0].re, offset.y + path[0].im);
} else {
cctx.lineTo(offset.x + path[i].re, offset.y + path[i].im);
}
}
cctx.stroke();
if (deg === RE.length - 1) {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(rAF);
} else {
deg++;
}
}